redis/46285.html">redis中的hash也是我們使用中的高頻數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),它的構(gòu)造基本上和編程語言中的HashTable,Dictionary大同小異,如果大家往后有什么邏輯需要用Dictionary存放的話,可以根據(jù)場景優(yōu)先考慮下redis哦。
一:常用方法
只要是一個數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),最基礎(chǔ)的永遠是CURD,redis中的insert和update,永遠只需要set來替代,比如下面的Hset,如下圖:

就好像Java中的類和方法,知道傳遞一些啥參數(shù)就OK了,就比如要說的HSet,它的格式如下:

接下來我在CentOS里面操作一下,
[administrator@localhost redis-3.0.5]$ src/redis-cli.0.0.1:6379> clear.0.0.1:6379> hset person name jack(integer) 1.0.0.1:6379> hset person age 20(integer) 1.0.0.1:6379> hset person sex famale(integer) 1.0.0.1:6379> hgetall person) "name") "jack") "age") "20") "sex") "famale".0.0.1:6379> hkeys person) "name") "age") "sex".0.0.1:6379> hvals person) "jack") "20") "famale".0.0.1:6379>
或許有人看了上面的console有一點疑惑,那就是前面有幾個參數(shù),比如person,name啦,然后才是value,其實在redis的這個層面,它永遠只有一個鍵,一個值,這個鍵永遠都是字符串對象,也就是SDS對象,而值的種類就多了,有字符串對象,有隊列對象,還有這篇的hash對象,往后的有序集合對象等等,如果你還不明白的話,轉(zhuǎn)化為Java語言就是。
Map<String,String> person=new HashMap<string,string>(); person.Add("name","jack"); ....調(diào)用方法就是這么的簡單,關(guān)鍵在于時不時的需要你看一看手冊,其實最重要的是了解下它在redis源碼中的原理就好了。
二:探索原理
hash的源代碼是在dict.h源代碼里面,枚舉如下:
typedef struct dictEntry { void *key; union { void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; double d; } v; struct dictEntry *next;} dictEntry;typedef struct dictType { unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key); void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);} dictType;/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we * implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new 0. */typedef struct dictht { dictEntry **table; unsigned long size; unsigned long sizemask; unsigned long used;} dictht;typedef struct dict { dictType *type; void *privdata; dictht ht[2]; long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */} dict;/* If safe is set to 1 this is a safe iterator, that means, you can call * dictAdd, dictFind, and other functions against the dictionary even while * iterating. Otherwise it is a non safe iterator, and only dictNext() * should be called while iterating. */typedef struct dictIterator { dict *d; long index; int table, safe; dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry; /* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection. */ long long fingerprint;} dictIterator;上面就是我們使用hash的源代碼數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),接下來我來擼一擼其中的邏輯關(guān)系。
dict結(jié)構(gòu)
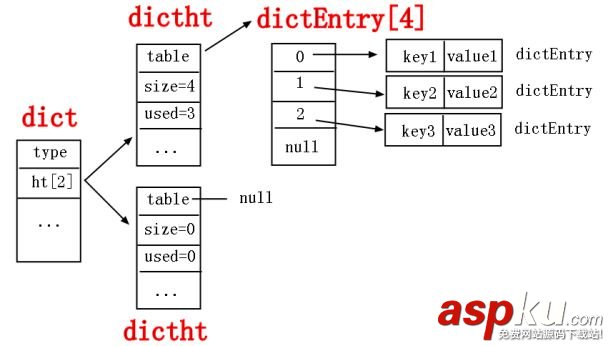
typedef struct dict { dictType *type; void *privdata; dictht ht[2]; long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */ } dict;這個結(jié)構(gòu)是hash的真正的底層數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),可以看到其中有5個屬性。
<1> dictType *type
可以看到它的類型是dictType,從上面你也可以看到,它是有枚舉結(jié)構(gòu)定義的,如下:
typedef struct dictType { unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key); void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj); } dictType;從上面這個數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)中你可以看到里面都是一些方法,但是有一個非常重要的方法,那就是第一個hashFunction,可以看到它就是計算hash值的,跟Java中的求hash值差不多。
<2> dictht ht[2]
你可能會疑問,為什么這個屬性是2個大小的數(shù)組呢,其實正真使用的是ht[0],而ht[1]是用于擴容hash表時的暫存數(shù)組,這一點也很奇葩,同時也很精妙,redis為什么會這么做呢???仔細想想你可能會明白,擴容有兩種方法,要么一次性擴容,要么漸進性擴容,后面這種擴容是什么意思呢?就是我在擴容的同時不影響前端的CURD,我慢慢的把數(shù)據(jù)從ht[0]轉(zhuǎn)移到ht[1]中,同時rehashindex來記錄轉(zhuǎn)移的情況,當全部轉(zhuǎn)移完成之后,將ht[1]改成ht[0]使用,就這么簡單。
dicth結(jié)構(gòu)
typedef struct dictht {dictEntry **table; unsigned long size; unsigned long sizemask; unsigned long used; } dictht;<1> dictEntry **table;
從上面這個結(jié)構(gòu)體中,你可以看到一個非常重要的屬性: dictEntry **table, 其中table是一個數(shù)組,數(shù)組類型是dictEntry,既然是一個數(shù)組,那后面的三個屬性就好理解了,size是數(shù)組的大小,sizemask和數(shù)組求模有關(guān),used記錄數(shù)組中已使用的大小,現(xiàn)在我們把注意力放在dictEntry這個數(shù)組實體類型上面。
dictEntry結(jié)構(gòu)
typedef struct dictEntry { void *key; union { void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; double d; } v; struct dictEntry *next; } dictEntry;從這個數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)上面你可以看到有三個大屬性。
第一個就是: *key:它就是hash表中的key。
第二個就是: union的*val 就是hash的value。
第三個就是: *next就是為了防止hash沖突采用的掛鏈手段。
如果總結(jié)上面描述的話,我可以畫出如下的hash結(jié)構(gòu)圖。
新聞熱點
疑難解答
圖片精選