主要思路是通過父布局的onTouch(),方法,獲取滑動到的位置和點擊下的位置,再去設(shè)置子view的位置。我的代碼中考慮了在邊緣情況。需要注意的是,使用RelativeLayout,以imageView為例。從測試結(jié)果來看,bottomMargin 和rightMargin 性能非常差,最好還是用leftMargin與topMargin定位。
下面是運行效果:
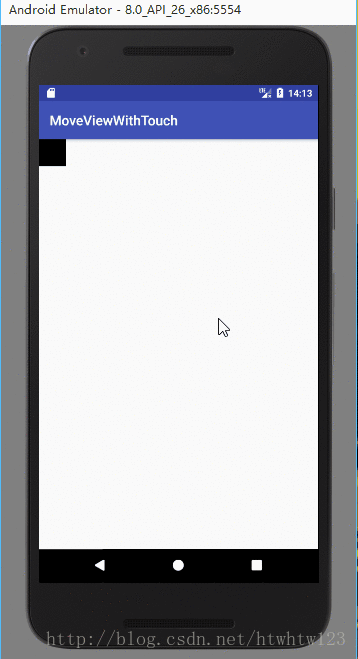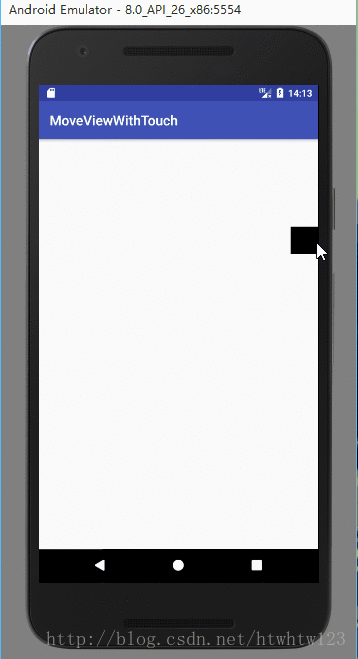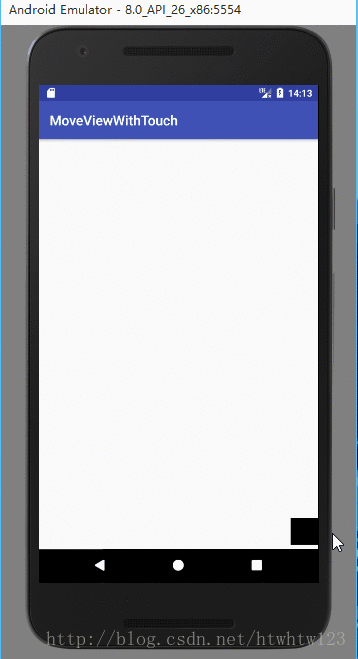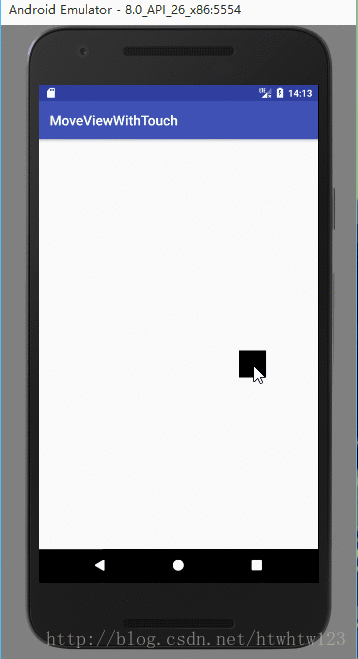
布局文件里面就是一個Relativelayout中有一個ImageView。如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/relativeLayout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.xingyi.moveviewwithtouch.MainActivity"><ImageView android:id="@+id/imageView" android:layout_width="40dp" android:layout_height="40dp" android:background="@android:color/black"/></RelativeLayout>
Java代碼如下,這里考慮了邊緣位置滑動的效果。如果考慮,在最左邊緣imageView會有一半在屏幕之外,在最右邊緣會縮小,直到看不見。
package com.xingyi.moveviewwithtouch;import android.os.Bundle;import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.view.MotionEvent;import android.view.View;import android.widget.ImageView;import android.widget.RelativeLayout;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { ImageView imageView; RelativeLayout relativeLayout; int heightRL,widthRL; int halfHeight,halfWidth; boolean first=true; private int widthImg; private int heightImg; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); initView(); } //初始化視圖 private void initView() { imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageView); relativeLayout = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.relativeLayout); //獲取滑動瞬間位置和點擊瞬間位置,并移動imageview relativeLayout.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() { @Override public boolean onTouch(View view, MotionEvent motionEvent) { switch (motionEvent.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: moveView(imageView, motionEvent.getX(), motionEvent.getY()); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: getWidthAndHeight(); moveView(imageView, motionEvent.getX(), motionEvent.getY()); break; default: break; } return true; } }); } //因為不能在初始化視圖時獲得長寬,而每次計算一次長寬又影響性能 private void getWidthAndHeight(){ if(first){ widthRL=relativeLayout.getWidth(); heightRL=relativeLayout.getHeight(); widthImg=imageView.getWidth(); heightImg=imageView.getHeight(); halfWidth = imageView.getWidth() / 2;//imageView寬度的一半 halfHeight = imageView.getHeight() / 2;//imageView高度的一半 first=false; } } //滑動瞬間,將x和y分別作imageView的中心點到relativeLayout最左和頂端距離 private void moveView(View view, float x, float y) { RelativeLayout.LayoutParams params = (RelativeLayout.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams(); //設(shè)置水平位置 if (x < halfWidth) {//左邊緣 params.leftMargin = 0;//設(shè)置imageview到左端距離為0 } else if (x > widthRL- halfWidth) { params.leftMargin = widthRL-widthImg;//設(shè)置imageview左端到左端端距離(params.rightMargin的性能非常糟糕) } else { params.leftMargin = (int) (x - halfWidth);//imageview左端到relativelayout左端距離 } //設(shè)置豎直位置 if (y < halfHeight) { params.topMargin = 0; } else if (y > heightRL - halfHeight) { params.topMargin = heightRL-widthImg;//params.bottomMargin的性能非常糟糕 } else { params.topMargin = (int) (y - halfHeight); } view.setLayoutParams(params); }}總結(jié)
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的Android view隨觸碰滑動效果,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時回復(fù)大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對VEVB武林網(wǎng)網(wǎng)站的支持!
新聞熱點
疑難解答
圖片精選