本文著重介紹sql server 2005新增加的row-number排序函數(shù),它會(huì)根據(jù)你指定的分類標(biāo)準(zhǔn)將結(jié)果數(shù)據(jù)集進(jìn)行分類,同時(shí)給數(shù)據(jù)集分配連續(xù)的頁(yè)面,供大家參考!
分頁(yè),就是按照某種規(guī)則顯示分組數(shù)據(jù)集,但是在sql server 中,分頁(yè)并不是十分容易就能夠?qū)崿F(xiàn)。在過去,開發(fā)人員通常需要自己編寫程序,使用臨時(shí)表格來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)分頁(yè)功能,或者將所有的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)果集返回到客戶端,在客戶端進(jìn)行分頁(yè)操作。從開發(fā)人員或者dba的角度來(lái)看,兩種方法都不能令人滿意。
隨著sql server的發(fā)布,其中的一些排序函數(shù)使得開發(fā)人員編寫數(shù)據(jù)分頁(yè)程序變得更加簡(jiǎn)單和高效。這些新的排序函數(shù)提供了統(tǒng)計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)集的數(shù)目,對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)集歸類,按照某種標(biāo)準(zhǔn)對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)集排序等功能。在這篇文章中,我將著重介紹新增加的row-number排序函數(shù),它會(huì)根據(jù)你指定的分類標(biāo)準(zhǔn)將結(jié)果數(shù)據(jù)集進(jìn)行分類,同時(shí)給數(shù)據(jù)集分配連續(xù)的頁(yè)面。
一個(gè)分頁(yè)的實(shí)例
我總是喜歡通過例子來(lái)介紹如何使用新技術(shù),所以讓我們來(lái)看看如何設(shè)計(jì)一個(gè)存儲(chǔ)程序,使用row_number這一新函數(shù)來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)的自動(dòng)分頁(yè)。
首先,需要定義一些數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)。我們定義一個(gè)saleshistory表格,它包含的數(shù)據(jù)是我們?cè)诰W(wǎng)上售出產(chǎn)品的銷售記錄。包括一些常見的銷售信息,例如,所售產(chǎn)品、售出日期、產(chǎn)品售出價(jià)格等。下面的腳本就是創(chuàng)建這樣的一個(gè)表格:
code:
if object_id('saleshistory','u') > 0
drop table saleshistory
create table saleshistory
(
saleid int identity(1,1),
product varchar(30),
saledate smalldatetime,
saleprice money
)運(yùn)行列表a中的腳本則在上面創(chuàng)建的saleshistory表中添加一些例子數(shù)據(jù)。
|||code:
列表a
declare @i smallint
set @i = 1
while (@i <=100)
begin
insert into saleshistory
(product, saledate, saleprice)
values
('computer', dateadd(mm, @i, '3/11/1919'), datepart(ms, getdate()) + (@i + 57) )
insert into saleshistory
(product, saledate, saleprice)
values
('bigscreen', dateadd(mm, @i, '3/11/1927'), datepart(ms, getdate()) + (@i + 13) )
insert into saleshistory
(product, saledate, saleprice)
values
('pooltable', dateadd(mm, @i, '3/11/1908'), datepart(ms, getdate()) + (@i + 29) )
set @i = @i + 1
end現(xiàn)在數(shù)據(jù)表中已經(jīng)具有實(shí)例數(shù)據(jù)。接下來(lái)我們看看如何調(diào)用程序來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)的分頁(yè)顯示。列表b包含這個(gè)程序的腳本內(nèi)容。這個(gè)程序含有兩個(gè)參數(shù):1.頁(yè)面大小(給定頁(yè)面要顯示的數(shù)據(jù)記錄數(shù)目)2.目標(biāo)頁(yè)面(返回該頁(yè)的數(shù)據(jù)記錄)。
code:
列表b
create procedure usp_salesrecords
(
@pagesize float,
@targetpage smallint
)
as
begin
with sales_cte(pagenumber, saleid, product, saledate, saleprice)
as
(
select
ceiling((row_number() over (order by saledate asc))/@pagesize) as pagenumber,
saleid, product, saledate, saleprice
from saleshistory from saleshistory
)
select
pagenumber, saleid, product, saledate, saleprice
from
sales_cte
where
pagenumber = @targetpage
endcreate procedure usp_salesrecords
(
@pagesize float,
@targetpage smallint
)
as
begin
with sales_cte(pagenumber, saleid, product, saledate, saleprice)
as
(
select
ceiling((row_number() over (order by saledate asc))/@pagesize) as pagenumber,
saleid, product, saledate, saleprice
from saleshistory from saleshistory
)
select
pagenumber, saleid, product, saledate, saleprice
from
sales_cte
where
pagenumber = @targetpage
end如果你剛剛開始使用sql server,可能會(huì)不熟悉以“with”開頭的聲明語(yǔ)句。這條語(yǔ)句會(huì)調(diào)用sql server中的一個(gè)新屬性,我們稱之為common table expression(cte),從本質(zhì)上來(lái)說(shuō),我們可以將cte看作是高版本的臨時(shí)表。
|||分頁(yè)的實(shí)質(zhì)就是cte中的tsql語(yǔ)句。在下面的選擇語(yǔ)句中,我使用了一個(gè)新的排序函數(shù)——row_number(這一函數(shù)很容易使用,你只需要給row_number函數(shù)提供一個(gè)域名作為參數(shù),row_number會(huì)用它來(lái)進(jìn)行分頁(yè))。隨后,我使用@pagesize參數(shù)來(lái)劃分每頁(yè)的行數(shù)以及每頁(yè)的最大行數(shù)值。
例如,假設(shè)現(xiàn)在有一個(gè)包含三條記錄的數(shù)據(jù)集,并設(shè)計(jì)每頁(yè)顯示兩條記錄,那么頭兩條記錄將會(huì)在第一頁(yè)顯示,因?yàn)槊宽?yè)的行數(shù)必須小于或者等于第一個(gè)變量值。第三條記錄將會(huì)在第二頁(yè)顯示,因?yàn)槊宽?yè)的可顯示最大行數(shù)值應(yīng)該小于2但是又大于1。
可以使用下面的腳本調(diào)用存儲(chǔ)程序:
code:
execute usp_salesrecords
@pagesize = 3,
@targetpage = 2執(zhí)行程序后的返回結(jié)果如下:
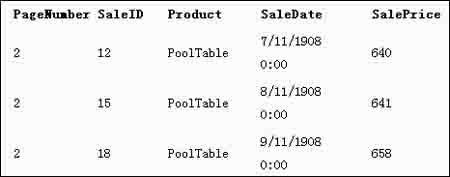
圖1
就如你所看到的,程序執(zhí)行后將會(huì)返回一頁(yè)的數(shù)據(jù),包含三條記錄,而且返回的是第二頁(yè)的數(shù)據(jù)集。
需要注意的一點(diǎn)
一般來(lái)說(shuō),有兩種方法完成數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)果的分頁(yè):在數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)層實(shí)現(xiàn)和不在數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)層實(shí)現(xiàn)。可以在客戶端實(shí)現(xiàn)分頁(yè),但是這樣做的時(shí)候,所有的數(shù)據(jù)都會(huì)返回到客戶端,而且在進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)分析的時(shí)候就決定了頁(yè)面數(shù)目。在早期版本的sql server中,可以在數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)層實(shí)現(xiàn)分頁(yè),但是需要臨時(shí)表和表變量。如果上面的例子沒有使用cte來(lái)進(jìn)行分頁(yè)的話,分頁(yè)程序就不會(huì)那么簡(jiǎn)單。之所以這么簡(jiǎn)單就是因?yàn)槭褂昧藃ow_number函數(shù)的強(qiáng)大功能。在以后的文章中,我將會(huì)大概介紹一下其它三種排列函數(shù),并展示它們提供的一些靈活易用的函數(shù)功能。
|
新聞熱點(diǎn)
疑難解答
圖片精選