對重構的強大支持是軟件開發人員喜愛eclipse的一個最為重要的原因。而eclipse還有一個至少和重構不相上下的優點,那就是其近乎無懈可擊的可擴展性。這兩者的結合意味著我們可以根據自己的需要來創建展新的重構功能。

package main;
public class testsomething {
@test(timeout=500)
public void testsomething(){}
}
org.eclipse.jface.text
org.eclipse.ltk.core.refactoring
org.eclipse.ltk.ui.refactoring
org.eclipse.jdt
org.eclipse.jdt.core
manifest-version: 1.0
bundle-manifestversion: 2
bundle-name: annotation plug-in
bundle-symbolicname: manage.annotation; singleton:=true
bundle-version: 1.0.0
bundle-activator: manage.annotation.annotationplugin
bundle-localization: plugin
require-bundle: org.eclipse.ui,
org.eclipse.core.runtime,
org.eclipse.jface.text,
org.eclipse.ltk.core.refactoring,
org.eclipse.ltk.ui.refactoring,
org.eclipse.jdt,
org.eclipse.jdt.core
eclipse-autostart: true
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<?eclipse version="3.0"?>
<plugin>
<extension
point="org.eclipse.ui.actionsets">
<actionset
label="annotation action set"
visible="true"
id="manage.annotation.actionset">
<menu
label="%refactoring.menu.label"
path="source"
id="org.eclipse.jdt.ui.refactoring.menu">
<separator name="reorggroup"/>
</menu>
<action
class="manage.annotation.actions.annotationmanageaction"
icon="icons/sample.gif"
id="manage.annotation.actions.annotationmanageaction"
label="%annotation.manage"
menubarpath="org.eclipse.jdt.ui.refactoring.menu/reorggroup"
toolbarpath="reorggroup"
tooltip="manage annotation in java project"/>
</actionset>
</extension>
</plugin>
public void selectionchanged(iaction action, iselection selection) {
if (selection.isempty())
select = null;
else if (selection instanceof istructuredselection) {
istructuredselection strut = ((istructuredselection) selection);
if (strut.size() != 1)
select = null;
if (strut.getfirstelement() instanceof ijavaelement)
select = (ijavaelement) strut.getfirstelement();
} else
select = null;
action.setenabled(select != null);
}
操作的執行是在annotationmanageaction的run函數中實現的,例如在本文的工程中,就是彈出refactoringwizard對話框,指導用戶完成重構的工作,這些我們將在下面的章節中講述。
擴展refactoring類
通過前面系統構架的介紹,大家知道了refactoring和refactoringwizard是完成eclipse重構功能的基礎類。在創建好插件工程后,我們就通過擴展refactoring來實現具體的功能。
refactoring是所有支持代碼轉化的類的抽象父類,它在整個流程中與refactoringwizard交互以完成重構的功能,起著非常重要的作用。這些類需要提供以下兩類方法:
用于條件檢查的方法,判斷重構操作大體而言能否執行,以及具體的轉化能否完成;
創建change對象的方法,change對象描述了所有將要執行的對當前代碼的修改操作。
refactoring類的典型流程如下所示:
1. 具體的refactoring類被創建。
2. 獲得用戶選擇的要進行重構的對象,初始化該refactoring類。這個由具體的實現類給出相應的方法。
3. 在重構操作開始執行時,首先調用refactoring的checkinitialconditions(iprogressmonitor) 基于用戶選擇的對象做一個的初始檢查,這個通常由界面自動執行。返回refactoringstatus.fatal表明初始檢查沒有通過,重構操作不能繼續。
4. 獲得進行重構的其他參數,比如,對重命名操作來說就是指新名字。這個通常是由界面根據用戶的輸入提供的。由具體的實現類給出相應的方法。
5. 獲得用戶輸入參數后,調用refactoring的checkfinalconditions(iprogressmonitor)進行剩下的檢查,這個通常由界面自動執行,返回refactoringstatus.fatal表明最后的檢查沒有通過,重構操作不能繼續。
6. 調用refactoring的createchange(iprogressmonitor)獲得change對象,這個通常由界面自動執行,界面可以根據change對象顯示預覽界面。
基于以上的介紹,為了實現本文工程中的重構操作,我們需要擴展refactoring類,為它增加一個構造函數,并且具體實現checkinitialconditions、checkfinalconditions和createchange三個函數。
首先通過菜單file -> new->class彈出創建類的對話框,輸入包名manage.annotation.refactor,類名annotationrefactoring,輸入父類org.eclipse.ltk.core.refactoring.refactoring,選中"繼承抽象方法"復選框,點擊完成按鈕,一個擴展了refactoring的最基本的類annotationrefactoring就被創建出來了。
首先為其增加構造函數,以用戶選擇的java模型元素作為參數。refactoring分析這個參數以得到所有相關的可寫java文件,作為重構操作的對象,如果該模型元素包含在java文件中,則找到包含它的文件節點;如果該模型元素包含java文件,則找到它的所有子java文件。構造函數代碼如下:
清單 6
public annotationrefactoring(ijavaelement element) {
while (element.getelementtype() > ijavaelement.compilation_unit) {
element = element.getparent();
if (element == null)
return;
}
if (element.getelementtype() == ijavaelement.compilation_unit) {
if (!element.isreadonly())
compilationunits.add(element);
}
if (element.getelementtype() < ijavaelement.compilation_unit)
findwritablecompilationunits(element);
}
public refactoringstatus checkinitialconditions(iprogressmonitor pm)
throws coreexception, operationcanceledexception {
return refactoringstatus.createinfostatus("initial condition is ok!");
}
public refactoringstatus checkfinalconditions(iprogressmonitor pm)
throws coreexception, operationcanceledexception {
collectchanges();
if (fchangemanager.size() == 0)
return refactoringstatus.createfatalerrorstatus("no testing methods found!");
else return refactoringstatus.createinfostatus("final condition is ok!");
}
使用ast構造change對象
當我們找到了修改的位置時,我們有兩個選擇:
1. 通過iscanner接口掃描代碼,然后通過ibuffer接口直接修改代碼
2. 通過遍歷和編輯ast樹進行結構化的修改
developerworks提供的文章《擴展eclipse的java開發工具》中,給出了使用ibuffer接口的例子。現在我們要講述使用ast來遍歷和修改java源代碼的方法。
ast是abstract syntax tree的縮寫。它是eclipse中的java開發環境(jdt)為我們提供的極為強大的源代碼解析和編輯工具。
在使用ast樹提供的功能之前,我們首先要創建ast樹。由于ast樹的構建是一項費時的操作,jdt缺省情況下不將源代碼解析為ast樹。下面的代碼演示了獲得一個icompilationunit對應的ast樹的過程。在jdt提供的api中,icompilationunit接口用于表示一個可以被編譯的源代碼文件。在我們提供的例子程序中,我們通過下面的代碼將整個文件解析成為了一顆ast樹。
清單 9
astparser parser = astparser.newparser(ast.jls3);
parser.setsource(cu);
astnode root = parser.createast(null);
private void getmethods(astnode cuu, final list methods) {
cuu.accept(new astvisitor() {
public boolean visit(methoddeclaration node) {
methods.add(node);
return false;
}
});
}
private boolean collectchanges(compilationunit root,methoddeclaration method) {
if (method.getname().getfullyqualifiedname().startswith("test")) {
ast ast = method.getast();
if (needtimeout) {
normalannotation na = ast.newnormalannotation();
na.settypename(ast.newsimplename("test"));
membervaluepair pair = ast.newmembervaluepair();
pair.setname(ast.newsimplename("timeout"));
pair.setvalue(ast.newnumberliteral("500"));
na.values().add(pair);
method.modifiers().add(0, na);
} else {
markerannotation na = ast.newmarkerannotation();
na.settypename(ast.newsimplename("test"));
method.modifiers().add(0, na);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
root.recordmodifications();
//在這里修改ast樹…
textedit edits = root.rewrite(document, cu.getjavaproject()
.getoptions(true));
textfilechange change = new textfilechange("", (ifile) cu
.getresource());
change.setedit(edits);
public change createchange(iprogressmonitor pm) throws coreexception,operationcanceledexception {
change[] changes = new change[fchangemanager.size()];
system.arraycopy(fchangemanager.toarray(), 0, changes, 0,fchangemanager.size());
compositechange change = new compositechange("add @override annotation", changes);
return change;
}
擴展refactoringwizard 框架
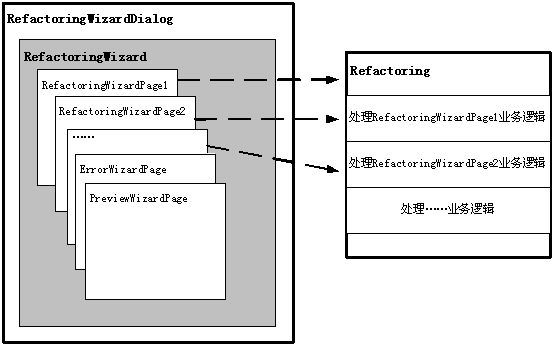
eclipse中的refactoringwizard框架擴展了eclipse的wizard框架,關于wizard框架的介紹可以在eclipse的幫助系統中找到,這里我們僅從oo設計和架構的角度探討一下refactoringwizard框架。
我們從wizard相關的幾個類開始:
1. wizardpage類
wizardpage是一個包含了多個界面元素(比如文本框text,按鈕button)的一個界面組合部分。各個page之間是獨立的,是可以動態加載的。wizardpage類的職責有:
·組合swt界面元素,構造出一個界面頁。
·定義本身界面元素的操作行為。
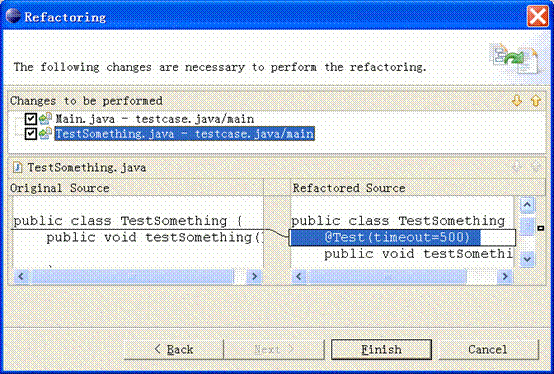
在refactoringwizard框架中預設了兩個通用的屬性頁:previewwizardpage和errorwizardpage。previewwizardpage類是用來預覽重構后的修改,對比代碼或其他資源的變化。errorwizardpage類是用來處理條件檢查及錯誤狀態通知的。我們只需擴展refactoringwizard框架就可以自動獲取這兩項強大的功能。
2. wizard類
一個wizard就是一個裝載一系列wizardpage頁的容器,wizard類的職責有:
·裝載一系列wizardpage,構造出一個復雜的界面。
·裝載領域類來處理具體業務邏輯。(在refactoringwizard框架中這個類就是refactoring類)
維護wizardpage頁之間以及頁與領域類之間的數據傳遞和狀態共享。(在這里要補充一點,其實在具體refactoringwizard框架的實現中有專門的類來分擔這部分職責。)
我們的界面行為可以千變萬化(通過組合不同的wizardpage),而負責處理業務邏輯的領域類也可以獨立的變化,你可以隨意擴展wizard的界面功能(-對擴展開放),而不用修改現有refactoringwizard框架(-對修改封閉),這正是oo設計的最基本原則-ocp(open-close principle)。
3. wizarddialog類
這個對話框類的主要職責是構造一個完整的gui界面以及操作界面。它預設了一些按鈕(back,next,finish,cancel)等界面元素,它負責裝載wizard類,操作時通過按鈕back、next來在多個wizardpage之間切換。
下面我們給出refactoringwizard框架的架構圖:
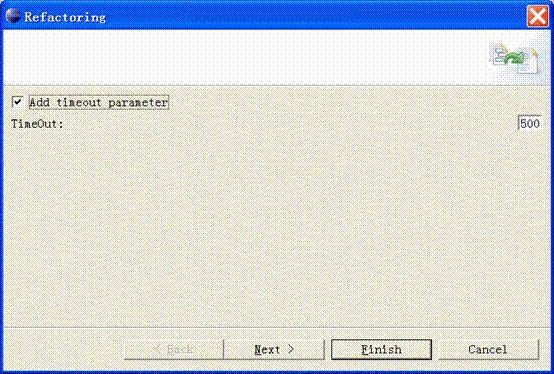
/**
* create composite to add ui elements
*/
public void createcontrol(composite parent) {
// define ui
composite composite = new composite(parent, swt.none);
gridlayout lay = new gridlayout();
lay.numcolumns = 2;
composite.setlayout(lay);
btncheck = new button(composite, swt.check);
btncheck.settext("add timeout parameter");
griddata gdbtncheck = new griddata();
gdbtncheck.horizontalspan = 2;
gdbtncheck.horizontalalignment = griddata.fill;
btncheck.setlayoutdata(gdbtncheck);
labname = new label(composite, swt.wrap);
labname.settext("timeout:");
griddata gdlabname = new griddata();
gdlabname.horizontalalignment = griddata.beginning;
gdlabname.grabexcesshorizontalspace = true;
labname.setlayoutdata(gdlabname);
txttimeout = new text(composite, swt.single | swt.border);
griddata gdtxttimeout = new griddata();
gdtxttimeout.horizontalalignment = griddata.end;
gdlabname.grabexcesshorizontalspace = true;
txttimeout.setlayoutdata(gdtxttimeout);
txttimeout.settext("500");
// init status
labname.setenabled(false);
txttimeout.setenabled(false);
// add listener
definelistener();
// 將composite納入框架的控制
setcontrol(composite);
dialog.applydialogfont(composite);
}
private void notifystatus(boolean valid, string message) {
//設置錯誤信息
seterrormessage(message);
//設置頁面完成狀態
setpagecomplete(valid);
}
private void setrefactoring(boolean selection, string text) {
annotationrefactoring refactoring = (annotationrefactoring) getrefactoring();
refactoring.setneedtimeout(true);
if(selection) {
refactoring.settimeout(integer.valueof(txttimeout.gettext()).intvalue());
}
}
public annotationrefactoringwizard(refactoring refactoring) {
super(refactoring, wizard_based_user_interface);
}
protected void adduserinputpages() {
page = new annotationrefactoringwizardpage("refactor annotation");
addpage(page);
}
public void run(iaction action) {
shell shell = window.getshell();
annotationrefactoring refactor = new annotationrefactoring(select);
annotationrefactoringwizard wizard = new annotationrefactoringwizard(refactor);
refactoringwizardopenoperation op = new refactoringwizardopenoperation(wizard);
try {
op.run(shell, "inserting @override annotation");
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
新聞熱點
疑難解答