最近鄰法和k-近鄰法
下面圖片中只有三種豆,有三個豆是未知的種類,如何判定他們的種類?
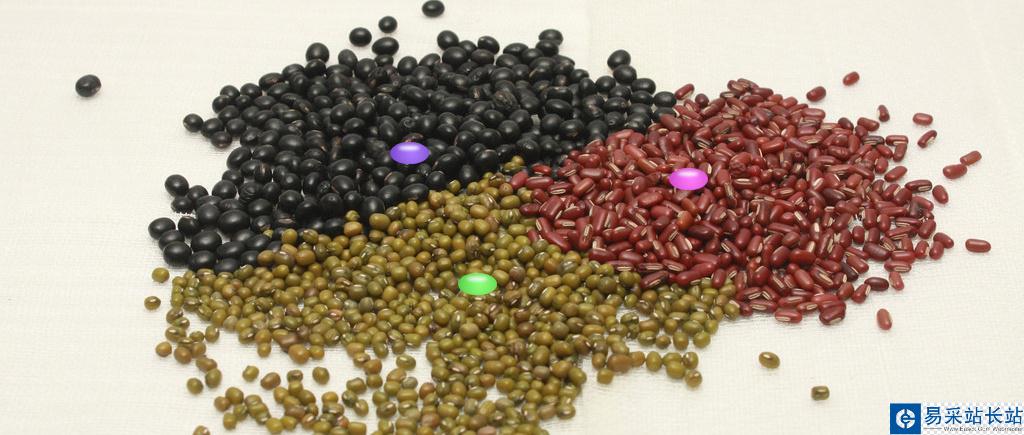

提供一種思路,即:未知的豆離哪種豆最近就認為未知豆和該豆是同一種類。由此,我們引出最近鄰算法的定義:為了判定未知樣本的類別,以全部訓練樣本作為代表點,計算未知樣本與所有訓練樣本的距離,并以最近鄰者的類別作為決策未知樣本類別的唯一依據。但是,最近鄰算法明顯是存在缺陷的,比如下面的例子:有一個未知形狀(圖中綠色的圓點),如何判斷它是什么形狀?
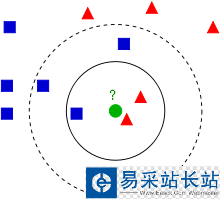
顯然,最近鄰算法的缺陷——對噪聲數據過于敏感,為了解決這個問題,我們可以可以把未知樣本周邊的多個最近樣本計算在內,擴大參與決策的樣本量,以避免個別數據直接決定決策結果。由此,我們引進K-最近鄰算法。K-最近鄰算法是最近鄰算法的一個延伸。基本思路是:選擇未知樣本一定范圍內確定個數的K個樣本,該K個樣本大多數屬于某一類型,則未知樣本判定為該類型。如何選擇一個最佳的K值取決于數據。一般情況下,在分類時較大的K值能夠減小噪聲的影響,但會使類別之間的界限變得模糊。待測樣本(綠色圓圈)既可能分到紅色三角形類,也可能分到藍色正方形類。如果k取3,從圖可見,待測樣本的3個鄰居在實線的內圓里,按多數投票結果,它屬于紅色三角形類。但是如果k取5,那么待測樣本的最鄰近的5個樣本在虛線的圓里,按表決法,它又屬于藍色正方形類。在實際應用中,K先取一個比較小的數值,再采用交叉驗證法來逐步調整K值,最終選擇適合該樣本的最優的K值。
KNN算法實現
算法基本步驟:
1)計算待分類點與已知類別的點之間的距離
2)按照距離遞增次序排序
3)選取與待分類點距離最小的k個點
4)確定前k個點所在類別的出現次數
5)返回前k個點出現次數最高的類別作為待分類點的預測分類
下面是一個按照算法基本步驟用python實現的簡單例子,根據已分類的4個樣本點來預測未知點(圖中的灰點)的分類:
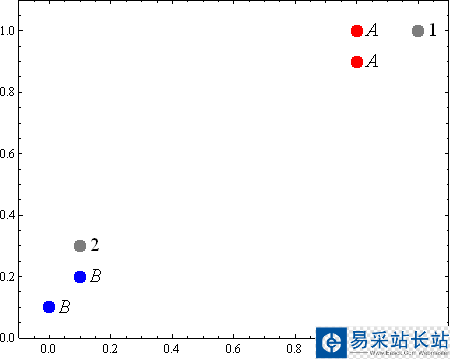
from numpy import * # create a dataset which contains 4 samples with 2 classes def createDataSet(): # create a matrix: each row as a sample group = array([[1.0, 0.9], [1.0, 1.0], [0.1, 0.2], [0.0, 0.1]]) labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'] # four samples and two classes return group, labels# classify using kNN (k Nearest Neighbors ) # Input: newInput: 1 x N# dataSet: M x N (M samples N, features)# labels: 1 x M # k: number of neighbors to use for comparison # Output: the most popular class label def kNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k): numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # shape[0] stands for the num of row ## step 1: calculate Euclidean distance # tile(A, reps): Construct an array by repeating A reps times # the following copy numSamples rows for dataSet diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet # Subtract element-wise squaredDiff = diff ** 2 # squared for the subtract squaredDist = sum(squaredDiff, axis = 1) # sum is performed by row distance = squaredDist ** 0.5 ## step 2: sort the distance # argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance) classCount = {} # define a dictionary (can be append element) for i in xrange(k): ## step 3: choose the min k distance voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]] ## step 4: count the times labels occur # when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount, get() # will return 0 classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1 ## step 5: the max voted class will return maxCount = 0 for key, value in classCount.items(): if value > maxCount: maxCount = value maxIndex = key return maxIndex if __name__== "__main__": dataSet, labels = createDataSet() testX = array([1.2, 1.0]) k = 3 outputLabel = kNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3) print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel testX = array([0.1, 0.3]) outputLabel = kNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3) print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel
新聞熱點
疑難解答