1.前言
版本:Python3.6.1 + PyQt5 + SQL Server 2012
以前一直覺得,機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)、手寫體識(shí)別這種程序都是很高大上很難的,直到偶然看到了這個(gè)視頻,聽了老師講的思路后,瞬間覺得原來這個(gè)并不是那么的難,原來我還是有可能做到的。
于是我開始順著思路打算用Python、PyQt、SQLServer做一個(gè)出來,看看能不能行。然而中間遇到了太多的問題,數(shù)據(jù)庫方面的問題有十幾個(gè),PyQt方面的問題有接近一百個(gè),還有數(shù)十個(gè)Python基礎(chǔ)語法的問題。但好在,通過不斷的Google,終于湊出了這么一個(gè)成品來。
最終還是把都湊在一個(gè)函數(shù)里的代碼重構(gòu)了一下,改寫成了4個(gè)模塊:
main.py、Learning.py、LearningDB.py、LearningUI.py
其中LearningDB實(shí)現(xiàn)python與數(shù)據(jù)庫的交互,LearningUI實(shí)現(xiàn)界面的交互,Learning繼承LearningUI類添加上了與LearningDB數(shù)據(jù)庫類的交互,最后通過main主函數(shù)模塊運(yùn)行程序。
手寫體識(shí)別的主要思路是將手寫的字,用一個(gè)列表記錄其所經(jīng)過的點(diǎn),劃分為一個(gè)九宮格,然后數(shù)每個(gè)格子中點(diǎn)的數(shù)目,將數(shù)目轉(zhuǎn)化為所占總點(diǎn)數(shù)的百分比。然后兩兩保存的九維數(shù),求他們之間的距離,距離越近代表越接近。
2.通過pymssql與數(shù)據(jù)庫的交互
因?yàn)槭褂贸绦蛑跋刃枰ū恚ū砦揖椭苯邮褂肧QL語句執(zhí)行了:
create database PyLearningDBdrop table table0create table table0(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table1create table table1(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table2create table table2(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table3create table table3(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table4create table table4(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table5create table table5(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table6create table table6(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table7create table table7(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table8create table table8(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)drop table table9create table table9(dim0 int not null,dim1 int not null,dim2 int not null,dim3 int not null,dim4 int not null,dim5 int not null,dim6 int not null,dim7 int not null,dim8 int not null)
LearningDB.py程序如下:
''' LearningDB類 功能:定義數(shù)據(jù)庫類,包含一個(gè)學(xué)習(xí)函數(shù)learn_data和一個(gè)識(shí)別函數(shù)identify_data 作者:PyLearn 博客: http://www.cnblogs.com/PyLearn/ 最后修改日期: 2017/10/18'''import mathimport pymssqlclass LearningDB(): def __init__(self): self.conn = pymssql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', user='sa', password='123', database='PyLearningDB', charset='utf8') self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() self.sql = '' self.distance = 0.0 self.conn.close() def learn_data(self, table, dim): ''' 學(xué)習(xí)數(shù)據(jù),將數(shù)據(jù)存到對(duì)應(yīng)的數(shù)據(jù)庫 table指定哪個(gè)表,dim是維度數(shù)組 ''' learn_result = False try: if table < 0 or table > 9: raise Exception("錯(cuò)誤!table的值為%d!" % table) for num in dim: if num < 0: raise Exception("錯(cuò)誤!dim的值不能小于0!") self.conn = pymssql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', user='sa', password='123', database='PyLearningDB', charset='utf8') self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() self.sql = 'insert into table%d values(%d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d)' %( table, dim[0], dim[1], dim[2], dim[3], dim[4], dim[5], dim[6], dim[7], dim[8]) self.cursor.execute(self.sql) self.conn.commit() learn_result = True except Exception as ex_learn: self.conn.rollback() raise ex_learn finally: self.conn.close() return learn_result def identify_data(self, test_data): ''' 識(shí)別數(shù)據(jù),將數(shù)據(jù)一一對(duì)比,返回最接近的近似值 ''' try: table_data = [] for i in range(10): table_data.append(self.__get_data(i, test_data)) #返回table_data中最小值的索引 return table_data.index(min(table_data)) except Exception as ex_identify: raise ex_identify def __get_data(self, table, test_data): ''' 取出table表中所有數(shù)據(jù) 并與測試數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行比較,返回最小值 如果table表中無數(shù)據(jù),則全部取0 ''' try: if table < 0 or table > 9: raise Exception("錯(cuò)誤!table的值不能為%d!" % table) self.conn = pymssql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', user='sa', password='123', database='PyLearningDB', charset='utf8') self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() self.sql = 'select * from table%d' % table self.cursor.execute(self.sql) receive_sql = self.cursor.fetchall() if not receive_sql: new_receive_sql = [(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)] else: new_receive_sql = receive_sql finally: self.conn.close() #計(jì)算最小值 dim_data = [] for receive_data in new_receive_sql: dim_data.append(self.__distance_data(test_data, receive_data)) #返回dimData中最小值 return min(dim_data) def __distance_data(self, test_data, table_data): ''' 求九維空間中兩點(diǎn)之間的距離 ''' self.distance = 0.0 for i in range(9): self.distance += (test_data[i] - table_data[i]) ** 2 return math.sqrt(self.distance)3.通過pyqt與界面的交互
LearningUI.py程序如下:
''' LearningUI類 功能:生成UI界面,以及定義事件處理方法 作者:PyLearn 博客: http://www.cnblogs.com/PyLearn/ 最后修改日期: 2017/10/18'''from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QPushButton, QLabel, QComboBox, QDesktopWidget)from PyQt5.QtGui import (QPainter, QPen, QFont)from PyQt5.QtCore import Qtclass LearningUI(QWidget): def __init__(self): super(LearningUI, self).__init__() self.__init_ui() #設(shè)置只有鼠標(biāo)按下時(shí)才跟蹤移動(dòng),否則不按的時(shí)候也在畫畫 self.setMouseTracking(False) #self.pos_xy保存所有繪畫的點(diǎn) self.pos_xy = [] #設(shè)置pos_x、pos_y方便計(jì)算 self.pos_x = [] self.pos_y = [] #設(shè)置關(guān)聯(lián)事件 self.btn_learn.clicked.connect(self.btn_learn_on_clicked) self.btn_recognize.clicked.connect(self.btn_recognize_on_clicked) self.btn_clear.clicked.connect(self.btn_clear_on_clicked) def __init_ui(self): ''' 定義UI界面: 三個(gè)按鈕:學(xué)習(xí)、識(shí)別、清屏 btn_learn、btn_recognize、btn_clear 一個(gè)組合框:選擇0-9 combo_table 兩條標(biāo)簽:請(qǐng)?jiān)谄聊豢瞻滋幱檬髽?biāo)輸入0-9中的某一個(gè)數(shù)字進(jìn)行識(shí)別! 2017/10/10 by PyLearn 一條輸出識(shí)別結(jié)果的標(biāo)簽 label_output ''' #添加三個(gè)按鈕,分別是學(xué)習(xí)、識(shí)別、清屏 self.btn_learn = QPushButton("學(xué)習(xí)", self) self.btn_learn.setGeometry(50, 400, 70, 40) self.btn_recognize = QPushButton("識(shí)別", self) self.btn_recognize.setGeometry(320, 400, 70, 40) self.btn_clear = QPushButton("清屏", self) self.btn_clear.setGeometry(420, 400, 70, 40) #添加一個(gè)組合框,選擇0-9 self.combo_table = QComboBox(self) for i in range(10): self.combo_table.addItem("%d" % i) self.combo_table.setGeometry(150, 400, 70, 40) #添加兩條標(biāo)簽 self.label_head = QLabel('請(qǐng)?jiān)谄聊豢瞻滋幱檬髽?biāo)輸入0-9中的某一個(gè)數(shù)字進(jìn)行識(shí)別!', self) self.label_head.move(75, 50) self.label_end = QLabel('2017/10/10 by PyLearn', self) self.label_end.move(375, 470) #添加一條輸出識(shí)別結(jié)果的標(biāo)簽 ''' setStyleSheet設(shè)置邊框大小、顏色 setFont設(shè)置字體大小、形狀、加粗 setAlignment設(shè)置文本居中 ''' self.label_output = QLabel('', self) self.label_output.setGeometry(50, 100, 150, 250) self.label_output.setStyleSheet("QLabel{border:1px solid black;}") self.label_output.setFont(QFont("Roman times", 100, QFont.Bold)) self.label_output.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter) ''' setFixedSize()固定了窗體的寬度與高度 self.center()將窗體居中顯示 setWindowTitle()設(shè)置窗體的標(biāo)題 ''' self.setFixedSize(550, 500) self.center() self.setWindowTitle('0-9手寫體識(shí)別(機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)中的"HelloWorld!")') def center(self): ''' 窗口居中顯示 ''' qt_center = self.frameGeometry() desktop_center = QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center() qt_center.moveCenter(desktop_center) self.move(qt_center.topLeft()) def paintEvent(self, event): ''' 首先判斷pos_xy列表中是不是至少有兩個(gè)點(diǎn)了 然后將pos_xy中第一個(gè)點(diǎn)賦值給point_start 利用中間變量pos_tmp遍歷整個(gè)pos_xy列表 point_end = pos_tmp 判斷point_end是否是斷點(diǎn),如果是 point_start賦值為斷點(diǎn) continue 判斷point_start是否是斷點(diǎn),如果是 point_start賦值為point_end continue 畫point_start到point_end之間的線 point_start = point_end 這樣,不斷地將相鄰兩個(gè)點(diǎn)之間畫線,就能留下鼠標(biāo)移動(dòng)軌跡了 ''' painter = QPainter() painter.begin(self) pen = QPen(Qt.black, 2, Qt.SolidLine) painter.setPen(pen) if len(self.pos_xy) > 1: point_start = self.pos_xy[0] for pos_tmp in self.pos_xy: point_end = pos_tmp if point_end == (-1, -1): point_start = point_end continue if point_start == (-1, -1): point_start = point_end continue painter.drawLine(point_start[0], point_start[1], point_end[0], point_end[1]) point_start = point_end painter.end() def mouseReleaseEvent(self, event): ''' 重寫鼠標(biāo)按住后松開的事件 在每次松開后向pos_xy列表中添加一個(gè)斷點(diǎn)(-1, -1) 然后在繪畫時(shí)判斷一下是不是斷點(diǎn)就行了 是斷點(diǎn)的話就跳過去,不與之前的連續(xù) ''' pos_test = (-1, -1) self.pos_xy.append(pos_test) self.update() def mouseMoveEvent(self, event): ''' 按住鼠標(biāo)移動(dòng):將移動(dòng)的點(diǎn)加入self.pos_xy列表 ''' #self.pos_x和self.pos_y總是比self.pos_xy少一到兩個(gè)點(diǎn),還不知道原因在哪 self.pos_x.append(event.pos().x()) self.pos_y.append(event.pos().y()) #中間變量pos_tmp提取當(dāng)前點(diǎn) pos_tmp = (event.pos().x(), event.pos().y()) #pos_tmp添加到self.pos_xy中 self.pos_xy.append(pos_tmp) self.update() def btn_learn_on_clicked(self): ''' 需要用到數(shù)據(jù)庫,因此在在子類中實(shí)現(xiàn) ''' pass def btn_recognize_on_clicked(self): ''' 需要用到數(shù)據(jù)庫,因此在在子類中實(shí)現(xiàn) ''' pass def btn_clear_on_clicked(self): ''' 按下清屏按鈕: 將列表賦值為空 將輸出識(shí)別結(jié)果的標(biāo)簽賦值為空 然后刷新界面,重新繪畫即可清屏 ''' self.pos_xy = [] self.pos_x = [] self.pos_y = [] self.label_output.setText('') self.update() def get_pos_xy(self): ''' 將手寫體在平面上分為9個(gè)格子 計(jì)算每個(gè)格子里點(diǎn)的數(shù)量 然后點(diǎn)的數(shù)量轉(zhuǎn)化為占總點(diǎn)數(shù)的百分比 接著返回一個(gè)數(shù)組dim[9] 橫軸依次是min_x、min2_x、max2_x、max_x 縱軸依次是min_y、min2_y、max2_y、max_y ''' if not self.pos_xy: return None pos_count = len(self.pos_x) max_x = max(self.pos_x) max_y = max(self.pos_y) min_x = min(self.pos_x) min_y = min(self.pos_y) dim = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] dis_x = (max_x - min_x) // 3 dis_y = (max_y - min_y) // 3 min2_x = min_x + dis_x min2_y = min_y + dis_y max2_x = max_x - dis_x max2_y = max_y - dis_y for i in range(len(self.pos_x)): if self.pos_y[i] >= min_y and self.pos_y[i] < min2_y: if self.pos_x[i] >= min_x and self.pos_x[i] < min2_x: dim[0] += 1 continue if self.pos_x[i] >= min2_x and self.pos_x[i] < max2_x: dim[1] += 1 continue if self.pos_x[i] >= max2_x and self.pos_x[i] <= max_x: dim[2] += 1 continue elif self.pos_y[i] >= min2_y and self.pos_y[i] < max2_y: if self.pos_x[i] >= min_x and self.pos_x[i] < min2_x: dim[3] += 1 continue if self.pos_x[i] >= min2_x and self.pos_x[i] < max2_x: dim[4] += 1 continue if self.pos_x[i] >= max2_x and self.pos_x[i] <= max_x: dim[5] += 1 continue elif self.pos_y[i] >= max2_y and self.pos_y[i] <= max_y: if self.pos_x[i] >= min_x and self.pos_x[i] < min2_x: dim[6] += 1 continue if self.pos_x[i] >= min2_x and self.pos_x[i] < max2_x: dim[7] += 1 continue if self.pos_x[i] >= max2_x and self.pos_x[i] <= max_x: dim[8] += 1 continue else: pos_count -= 1 continue #將數(shù)量轉(zhuǎn)化為所占百分比 for num in dim: num = num * 100 // pos_count return dim4.UI與數(shù)據(jù)庫的交互
Learning.py程序如下:
''' Learning類 功能:重寫LearningUI類中的兩個(gè)用到了數(shù)據(jù)庫的方法: 類中添加一個(gè)LearningDB類對(duì)象的數(shù)據(jù)成員self.learn_db 作者:PyLearn 博客: http://www.cnblogs.com/PyLearn/ 最后修改日期: 2017/10/18'''from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBoxfrom LearningUI import LearningUIfrom LearningDB import LearningDBclass Learning(LearningUI): ''' Learning實(shí)現(xiàn)btn_learn_on_clicked和btn_recognize_on_clicked兩個(gè)方法 ''' def __init__(self): super(Learning, self).__init__() #學(xué)習(xí)函數(shù)learn_data(table, dim)和一個(gè)識(shí)別函數(shù)identify_data(test_data) self.learn_db = LearningDB() def btn_learn_on_clicked(self): if not self.pos_xy: QMessageBox.critical(self, "注意", "請(qǐng)先寫入您要學(xué)習(xí)的數(shù)字!") return None #獲取要學(xué)習(xí)的數(shù)字learn_num learn_num = self.combo_table.currentIndex() #彈出確認(rèn)對(duì)話框 qbox = QMessageBox() qbox.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information) qbox.setWindowTitle("請(qǐng)確認(rèn)") qbox.setText("學(xué)習(xí)數(shù)字 %d ?" % learn_num) qbox.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No) qbox.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.No) qbox.button(QMessageBox.Yes).setText("是") qbox.button(QMessageBox.No).setText("否") reply = qbox.exec() #判斷對(duì)話框結(jié)果,執(zhí)行程序 if reply == QMessageBox.Yes: learn_result = False learn_dim = self.get_pos_xy() if learn_dim: learn_result = self.learn_db.learn_data(learn_num, learn_dim) else: print('get_pos_xy()函數(shù)返回空值') return None if learn_result: QMessageBox.about(self, "提示", "學(xué)習(xí)成功!") else: QMessageBox.about(self, "提示", "學(xué)習(xí)失敗!") else: return None def btn_recognize_on_clicked(self): #如果沒有進(jìn)行繪畫,警告后退出 if not self.pos_xy: QMessageBox.critical(self, "注意", "請(qǐng)先寫入您要識(shí)別的數(shù)字!") return None else: recognize_num = 0 recognize_dim = self.get_pos_xy() if recognize_dim: recognize_num = self.learn_db.identify_data(recognize_dim) else: print('recognize_dim為空') return None self.label_output.setText('%d' % recognize_num)5.最后的main主函數(shù)
''' 主函數(shù)main 功能:生成Learning對(duì)象,進(jìn)入主循環(huán) 作者:PyLearn 最后修改日期: 2017/10/18'''import sysfrom PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplicationfrom Learning import Learningif __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) py_learning = Learning() py_learning.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())
將以上4個(gè)程序放在同一個(gè)目錄下,直接執(zhí)行main.py就行了。
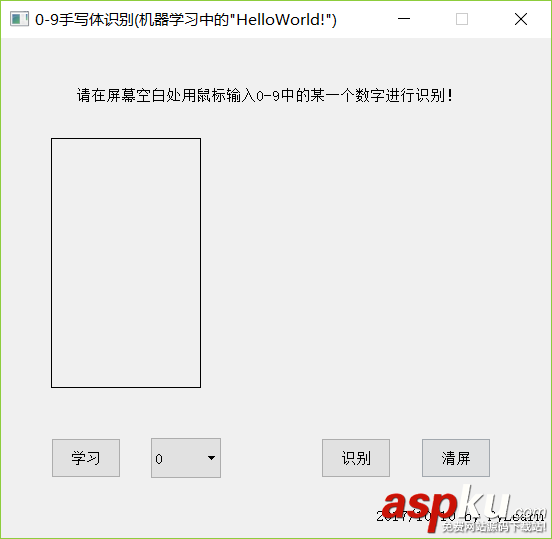
運(yùn)行界面如下:
學(xué)習(xí)數(shù)字4:
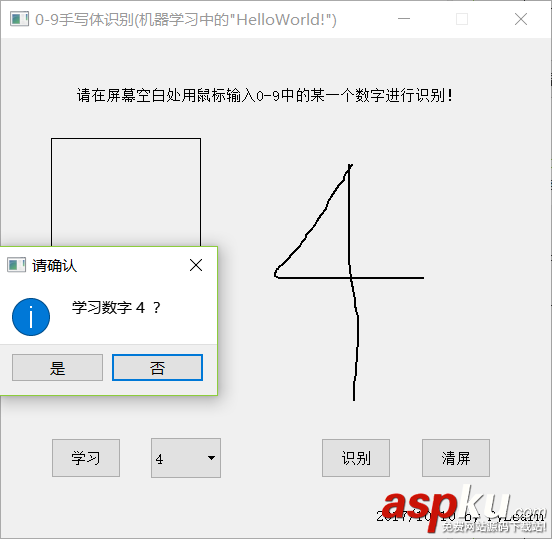
第一次運(yùn)行需要全部學(xué)習(xí)至少一次才能有一點(diǎn)正確率。
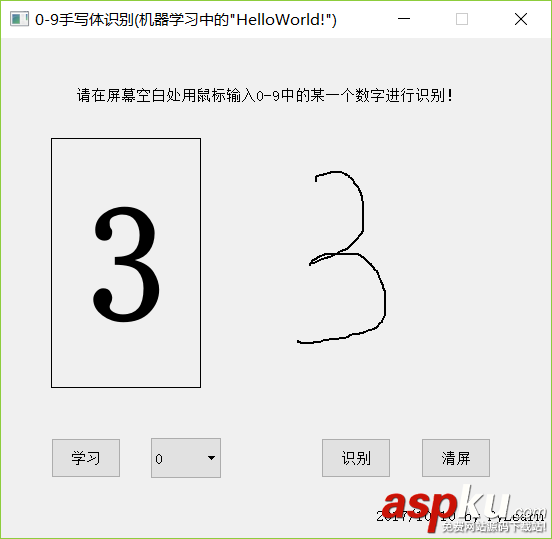
識(shí)別3:
以上這篇Python3實(shí)現(xiàn)簡單可學(xué)習(xí)的手寫體識(shí)別(實(shí)例講解)就是小編分享給大家的全部內(nèi)容了,希望能給大家一個(gè)參考,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林網(wǎng)。
新聞熱點(diǎn)
疑難解答
圖片精選