![]() Github下載完整代碼
Github下載完整代碼
https://github.com/rockingdingo/deepnlp/tree/master/deepnlp/pos
這篇文章中我們將基于Tensorflow的LSTM模型來實現序列化標注的任務,以NLP中的POS詞性標注為例實現一個深度學習的POS Tagger。文中具體介紹如何基于Tensorflow的LSTM cell單元來構建多層LSTM、雙向Bi-LSTM模型,以及模型的訓練和預測過程。對LSTM模型的基本結構和算法不熟悉的可以參考拓展閱讀里的一些資料。 完整版代碼可以在Github上找到:https://github.com/rockingdingo/deepnlp/tree/master/deepnlp/pos
我們使用的詞性標注POS的訓練集來源是url [人民日報1998年的新聞語料],格式為”充滿/v 希望/n 的/u 新/a 世紀/n ——/w 一九九八年/t”。具體的預處理過程包含以下步驟:
讀取訓練集數據:得到兩個列表Word和tag,其中word保存分詞,Tag保存對應的標簽;構建詞典:對詞進行Count并且按照出現頻率倒敘排列,建立字典表:word_to_id和tag_to_id 保存詞和標簽的id,未知詞的標簽即為UNKNOWN = "*";分別讀取訓練集train, dev和test數據集,將數據集的word列表和tag列表分別轉化為其對應的id列表。構建一個迭代器iterator, 每次返回讀取batch_size個詞和標簽的Pair對 (x,y)作為LSTM模型的輸入。 x代表詞ID的矩陣,y代表標簽ID的矩陣,形狀均為[batch_size, num_steps],代表batch_size組長度為num_steps的序列;矩陣中元素代表第x[i,j] 代表第i個batch下第j個詞的ID,如“132”(面條),y[i,j] 為其對應標簽的ID,如”3 ”(NN-名詞)。

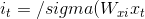 圖3 雙向LSTM結構 代碼4-2
圖3 雙向LSTM結構 代碼4-2lstm_fw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(size, forget_bias=0.0, state_is_tuple=True)lstm_bw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(size, forget_bias=0.0, state_is_tuple=True) cell_fw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([lstm_fw_cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True)cell_bw = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([lstm_bw_cell] * num_layers, state_is_tuple=True) initial_state_fw = cell_fw.zero_state(batch_size, data_type())initial_state_bw = cell_bw.zero_state(batch_size, data_type()) # Split to get a list of 'n_steps' tensors of shape (batch_size, n_input)inputs_list = [tf.squeeze(s, squeeze_dims=[1]) for s in tf.split(1, num_steps, inputs)] with tf.variable_scope("pos_bilstm"): outputs, state_fw, state_bw = tf.nn.bidirectional_rnn( cell_fw, cell_bw, inputs_list, initial_state_fw = initial_state_fw, initial_state_bw = initial_state_bw)前向傳播LSTM模型每次讀取當前步t的輸入Xt 和上一步的隱含層的向量h(t-1),通過LSTM內部結構的一系列計算得到相應的輸出。定義前向過程,通過for循環,每次輸入一個步t對應的詞向量 inputs[:, time_step, :],是一個3D的Tensor [batch_size, time_step, size] 。其中size為詞向量的維度。之后會將每一步的結果添加到outputs這個list中。
最后的全連接層:將output這個向量乘以softmax_w再加上偏移softmax_b,得到輸出部分的logits,最后利用tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 比較真實值的向量_targets和預測值的向量 logits,計算交叉熵cross-entropy的損失函數loss;
代碼5state = self._initial_statewith tf.variable_scope("pos_lstm"): for time_step in range(num_steps): if time_step > 0: tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables() (cell_output, state) = cell(inputs[:, time_step, :], state) outputs.append(cell_output) output = tf.reshape(tf.concat(1, outputs), [-1, size])softmax_w = tf.get_variable( "softmax_w", [size, target_num], dtype=data_type())softmax_b = tf.get_variable("softmax_b", [target_num], dtype=data_type())logits = tf.matmul(output, softmax_w) + softmax_bloss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, tf.reshape(targets, [-1]))關于損失函數Tensorflow中定義損失函數有:tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits() 和 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits()。 另外還有一個函數tf.nn.seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example()接收參數和sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits類似。 二者輸出結果一致,區別在于接收的輸入不同:
函數tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None)"sparse_softmax"這個函數輸入參數labels表示待擬合的標簽,形狀為 [batch_size] ,每個值為一個整形數值,int32或者int64, 代表了待預測標簽的ID,即每個樣本的標簽有且僅有一個。
函數tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, dim=-1, name=None)"softmax" 這個函數輸入參數labels形狀為[batch_size, num_classes],每個元素類型為float32或者 float64。每個樣本對應的標簽向量可以是One-Hot表示,即每個樣本只屬于一個類別;同時也可以是對應多個標簽soft softmax,即每個樣本的label不僅限于一個,而是給出符合每個類別的概率分布。這個函數支持一個樣本在多個類別下都有分布情況。
模型訓練過程 定義run_epoch函數:fetches:定義需要評估和取出的數值,這里我們要計算取出model.cost, model.final_state 和 eval_op三個參數,其中eval_op 為前向過程中定義的SGD梯度下降的操作符:self._train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars))feed_dict: 將每次迭代器返回的(x,y) Pair對的值,分別賦給input_data和target這兩個占位符。To Do: State[i].csession.run() 函數每次將feed_dict的數據輸入Graph模型,計算后返回fetches列表中定義的幾個變量[cost, state, _ ]。_ 代表了評估的Operator。
代碼6def run_epoch(session, model, word_data, tag_data, eval_op, verbose=False): """Runs the model on the given data.""" epoch_size = ((len(word_data) // model.batch_size) - 1) // model.num_steps start_time = time.time() costs = 0.0 iters = 0 state = session.run(model.initial_state) for step, (x, y) in enumerate(reader.iterator(word_data, tag_data, model.batch_size, model.num_steps)): fetches = [model.cost, model.final_state, eval_op] feed_dict = {} feed_dict[model.input_data] = x feed_dict[model.targets] = y for i, (c, h) in enumerate(model.initial_state): feed_dict[c] = state[i].c feed_dict[h] = state[i].h cost, state, _ = session.run(fetches, feed_dict) costs += cost iters += model.num_steps if verbose and step % (epoch_size // 10) == 10: print("%.3f perplexity: %.3f speed: %.0f wps" % (step * 1.0 / epoch_size, np.exp(costs / iters), iters * model.batch_size / (time.time() - start_time))) # Save Model to CheckPoint when is_training is True if model.is_training: if step % (epoch_size // 10) == 10: checkpoint_path = os.path.join(FLAGS.pos_train_dir, "pos.ckpt") model.saver.save(session, checkpoint_path) print("Model Saved... at time step " + str(step)) return np.exp(costs / iters)延伸閱讀
深語人工智能-技術博客: http://www.deepnlp.org/blog/tensorflow-lstm-pos/Python Package Index - deepnlp: Deep Learning NLP Pipeline implemented on Tensorflowhttps://pypi.python.org/pypi/deepnlpUnderstanding LSTM NetworksTensorflow:difference between sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits and softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits?
新聞熱點
疑難解答