一、概述
AutoEncoder大致是一個將數據的高維特征進行壓縮降維編碼,再經過相反的解碼過程的一種學習方法。學習過程中通過解碼得到的最終結果與原數據進行比較,通過修正權重偏置參數降低損失函數,不斷提高對原數據的復原能力。學習完成后,前半段的編碼過程得到結果即可代表原數據的低維“特征值”。通過學習得到的自編碼器模型可以實現(xiàn)將高維數據壓縮至所期望的維度,原理與PCA相似。
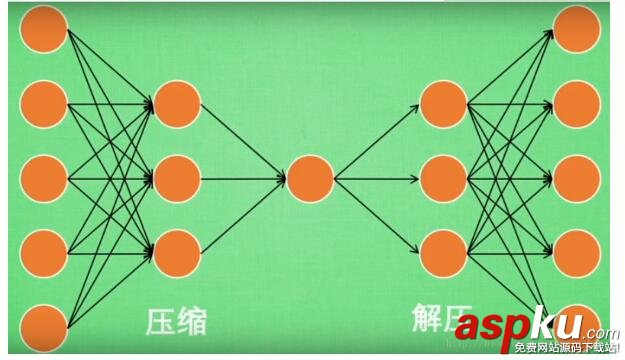
二、模型實現(xiàn)
1. AutoEncoder
首先在MNIST數據集上,實現(xiàn)特征壓縮和特征解壓并可視化比較解壓后的數據與原數據的對照。
先看代碼:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 導入MNIST數據 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=False) learning_rate = 0.01 training_epochs = 10 batch_size = 256 display_step = 1 examples_to_show = 10 n_input = 784 # tf Graph input (only pictures) X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_input]) # 用字典的方式存儲各隱藏層的參數 n_hidden_1 = 256 # 第一編碼層神經元個數 n_hidden_2 = 128 # 第二編碼層神經元個數 # 權重和偏置的變化在編碼層和解碼層順序是相逆的 # 權重參數矩陣維度是每層的 輸入*輸出,偏置參數維度取決于輸出層的單元數 weights = { 'encoder_h1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input, n_hidden_1])), 'encoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1, n_hidden_2])), 'decoder_h1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2, n_hidden_1])), 'decoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1, n_input])), } biases = { 'encoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])), 'encoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])), 'decoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])), 'decoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input])), } # 每一層結構都是 xW + b # 構建編碼器 def encoder(x): layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['encoder_h1']), biases['encoder_b1'])) layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['encoder_h2']), biases['encoder_b2'])) return layer_2 # 構建解碼器 def decoder(x): layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['decoder_h1']), biases['decoder_b1'])) layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['decoder_h2']), biases['decoder_b2'])) return layer_2 # 構建模型 encoder_op = encoder(X) decoder_op = decoder(encoder_op) # 預測 y_pred = decoder_op y_true = X # 定義代價函數和優(yōu)化器 cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(y_true - y_pred, 2)) #最小二乘法 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) with tf.Session() as sess: # tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from # 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12 if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: init = tf.initialize_all_variables() else: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # 首先計算總批數,保證每次循環(huán)訓練集中的每個樣本都參與訓練,不同于批量訓練 total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size) #總批數 for epoch in range(training_epochs): for i in range(total_batch): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) # max(x) = 1, min(x) = 0 # Run optimization op (backprop) and cost op (to get loss value) _, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs}) if epoch % display_step == 0: print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(c)) print("Optimization Finished!") encode_decode = sess.run( y_pred, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[:examples_to_show]}) f, a = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(10, 2)) for i in range(examples_to_show): a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(mnist.test.images[i], (28, 28))) a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(encode_decode[i], (28, 28))) plt.show() 代碼解讀:
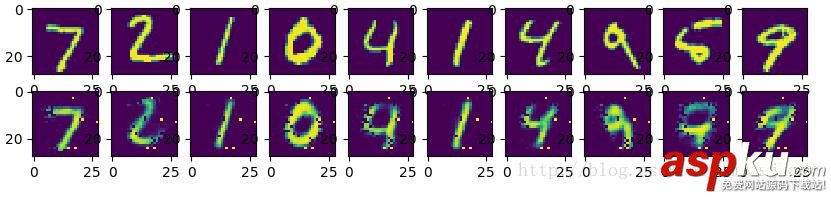
首先,導入將要使用到的各種庫和數據集,定義各個參數如學習率、訓練迭代次數等,清晰明了便于后期修改。由于自編碼器的神經網絡結構非常有規(guī)律性,都是xW + b的結構,故將每一層的權重W和偏置b的變量tf.Variable統(tǒng)一置于一個字典中,通過字典的key值更加清晰明了的描述。模型構建思路上,將編碼器部分和解碼器部分分開構建,每一層的激活函數使用Sigmoid函數,編碼器通常與編碼器使用同樣的激活函數。通常編碼器部分和解碼器部分是一個互逆的過程,例如我們設計將784維降至256維再降至128維的編碼器,解碼器對應的就是從128維解碼至256維再解碼至784維。定義代價函數,代價函數表示為解碼器的輸出與原始輸入的最小二乘法表達,優(yōu)化器采用AdamOptimizer訓練階段每次循環(huán)將所有的訓練數據都參與訓練。經過訓練,最終將訓練結果與原數據可視化進行對照,如下圖,還原度較高。如果增大訓練循環(huán)次數或者增加自編碼器的層數,可以得到更好的還原效果。
運行結果:
2. Encoder
Encoder編碼器工作原理與AutoEncoder相同,我們將編碼得到的低維“特征值”在低維空間中可視化出來,直觀顯示數據的聚類效果。具體地說,將784維的MNIST數據一步步的從784到128到64到10最后降至2維,在2維坐標系中展示遇上一個例子不同的是,在編碼器的最后一層中我們不采用Sigmoid激活函數,而是將采用默認的線性激活函數,使輸出為(-∞,+∞)。
完整代碼:
import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=False) learning_rate = 0.01 training_epochs = 10 batch_size = 256 display_step = 1 n_input = 784 X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_input]) n_hidden_1 = 128 n_hidden_2 = 64 n_hidden_3 = 10 n_hidden_4 = 2 weights = { 'encoder_h1': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_input, n_hidden_1],)), 'encoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hidden_1, n_hidden_2],)), 'encoder_h3': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hidden_2, n_hidden_3],)), 'encoder_h4': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hidden_3, n_hidden_4],)), 'decoder_h1': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hidden_4, n_hidden_3],)), 'decoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hidden_3, n_hidden_2],)), 'decoder_h3': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hidden_2, n_hidden_1],)), 'decoder_h4': tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hidden_1, n_input],)), } biases = { 'encoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])), 'encoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])), 'encoder_b3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_3])), 'encoder_b4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_4])), 'decoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_3])), 'decoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])), 'decoder_b3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])), 'decoder_b4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input])), } def encoder(x): layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['encoder_h1']), biases['encoder_b1'])) layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['encoder_h2']), biases['encoder_b2'])) layer_3 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_2, weights['encoder_h3']), biases['encoder_b3'])) # 為了便于編碼層的輸出,編碼層隨后一層不使用激活函數 layer_4 = tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_3, weights['encoder_h4']), biases['encoder_b4']) return layer_4 def decoder(x): layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['decoder_h1']), biases['decoder_b1'])) layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['decoder_h2']), biases['decoder_b2'])) layer_3 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_2, weights['decoder_h3']), biases['decoder_b3'])) layer_4 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_3, weights['decoder_h4']), biases['decoder_b4'])) return layer_4 encoder_op = encoder(X) decoder_op = decoder(encoder_op) y_pred = decoder_op y_true = X cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(y_true - y_pred, 2)) optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) with tf.Session() as sess: # tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from # 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12 if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: init = tf.initialize_all_variables() else: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size) for epoch in range(training_epochs): for i in range(total_batch): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) # max(x) = 1, min(x) = 0 _, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs}) if epoch % display_step == 0: print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(c)) print("Optimization Finished!") encoder_result = sess.run(encoder_op, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images}) plt.scatter(encoder_result[:, 0], encoder_result[:, 1], c=mnist.test.labels) plt.colorbar() plt.show() 實驗結果:
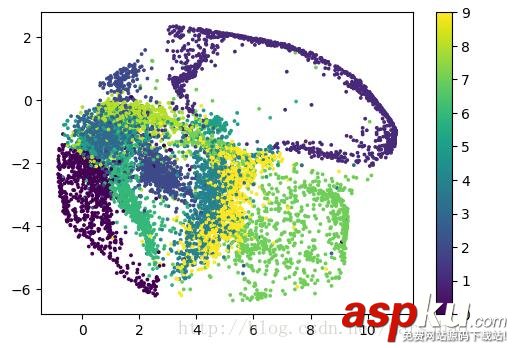
由結果可知,2維編碼特征有較好的聚類效果,圖中每個顏色代表了一個數字,聚集性很好。
當然,本次實驗所得到的結果只是對AutoEncoder做一個簡單的介紹,要想得到期望的效果,還應該設計更加復雜的自編碼器結構,得到區(qū)分性更好的特征。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林網。
新聞熱點
疑難解答